A Cross-sectional Baseline Survey on Random Blood Glucose (RBG) Screening at World Diabetes Day Commemoration Health Outreach amongst Adult Residents' of Gwagwalada Federal Capital Territory Abuja, Nigeria
Keywords:
Abuja FCT, Diabetes Mellitus, Gwagwalada, Health Screening, Random Blood, Glucose TestingAbstract
Background: Diabetes poses a significant public health challenge globally, necessitating proactive screening measures for early detection and intervention. Random Blood Glucose (RBG) screening is an effective tool for identifying abnormal glucose levels and assessing diabetes risks.
Methods: A cross-sectional baseline study was conducted in University of Abuja Teaching Hospital Gwagwalada Abuja (N8° 57ꞌ 1.4976ꞌꞌ, E 7° 3ꞌ 45.4212ꞌꞌ), Nigeria amongst 150 adult residents that voluntarily participated in the Health Awareness Talk, and granted verbal informed consent, with the goal of screening their random blood glucose. A random screening approach was adopted. The demographic data and views and response of volunteers were collected via structured questionnaires. The other clinical parameters of interest captured were subjects' RBG, Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, blood pressure and pulse rate. Data analysis was then carried out using SPSS for frequencies and percentages of responses. Descriptive and inferential statistical analyses were determined using chi square test. A p value of 0.05 or less represented the threshold for statistical significance.
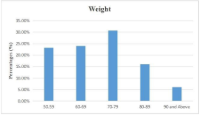
Results: The majority of participants were females (66%) aged 41–50 years (38.7%) with tertiary education (59.3%). Findings revealed that 5.7% of respondents had elevated RBG levels (>7.8 mmol/L), while a substantial proportion exhibited elevated BMI and waist circumference, indicating obesity-related risks. Alarmingly, 49.3% were unaware of their diabetes status, underscoring gaps in
health awareness.
Conclusion: The study highlighted the need for targeted public health interventions promoting regular screening and education, especially for middle-aged adults at risk of obesity-related conditions.
References
Nzeki, D.S., 2021. Determination of Blood Sugar Control Practices in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus During Covid-19 Pandemic Attending Kenyatta National Hospital (Doctoral dissertation, UON).
Muhammad F. Diabetes: A silent killer in Nigeria. Department of Public Health, Faculty of Allied Health Sciences, Daffodil International
University; 2020 May 26. Accepted 2020 Jun 25.
Etukumana EA, Puepet FH, Obadofin MO. (2014). Risk factors for diabetes mellitus among rural adults in Nigeria. Niger J Med. 23(3):213–9. PMID: 25185378
Bashir MA, Yahaya AI, Muhammad M, Yusuf AH, Mukhtar IG. (2021). Prediabetes burden in Nigeria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Public Health. 9: 762429. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.762429
West B, Parikh P, Arniella G, Horowitz CR. (2010). Observations and recommendations for community-based diabetes screenings. Diabetes Educ. 36 (6): 887 – 93. doi: 10.1177/0145721710386973. PMID: 21041537; PMCID: PMC3023957.
West KM. (1979). Community screening programs for diabetes? Diabetes Care. 2(4):381–4. doi: 10.2337/diacare.2.4.381. PMID: 510134.
Danraka, AM, Adegoke, VOO, Lawal, MM (2025). Assessment of Knowledge and Practices in Diabetes Management among Adults in
Gwagwalada Federal Capital Territory Abuja, Nigeria. MSI Journal of Medicine and Medical Research 2 (2). Pg 30 - 38
https://msipublishers.com/msijmmr/ DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.14946991
Pervez, A., Ahmer, A., Mahmud, O., Martins, R.S., Hussain, H., Nasir, S., Pirzada, S., Mustafa, M.A., Siddiqi, U., Zakaria, M. and Rizvi, N.A.,
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes in South Asia: A Systematic Review. Diabetes & Metabolic
Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, p.103094.
Ortiz-Martínez, M., González-González, M., Martagón, A.J., Hlavinka, V., Willson, R.C. and Rito-Palomares, M., 2022. Recent developments in biomarkers for diagnosis and screening of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Current diabetes reports, 22(3), pp.95-115.
Bhatia, V., Parida, S.P. and Chandanshive, P.D., 2021. Sociodemographic correlates of abnormal blood profile in tribal districts of Eastern India. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care, 10(8), pp.2822-2828.
Koivula, T., Lempiäinen, S., Laine, S., Sjöros, T., Vähä-Ypyä, H., Garthwaite, T., Löyttyniemi, E., Sievänen, H., Vasankari, T., Knuuti, J. and
Heinonen, I. H., 2022. Cross - sectional associations of body adiposity, sedentary behavior, and physical activity with hemoglobin and white blood cell count. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(21), p.14347.
Mutua, B.M., (2023). Red Cell Distribution Width as a Surrogate Marker of Haemoglobinopathies Among Patients in Aga Khan Hospital, Western Kenya (Doctoral dissertation, MMUST).
Uloko, A.E., Musa, B.M., Ramalan, M.A., Gezawa, I.D., Puepet, F.H., Uloko, A.T., et al. (2018). Prevalence and Risk Factors for Diabetes
Mellitus in Nigeria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Therapy 9(3), 1307–1316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-018-0441-1
Molenberg FJM, de Vries C., Burdorf A., Van Lenthe FJ (2021). A framework for exploring non- response patterns over time in health surveys.BMC MedicalResearch Methodology 21 (37).
Bowen, M.E., Xuan, L., Lingvay, I. and Halm, E.A., (2015). Random blood glucose: a robust risk factor for type 2 diabetes. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 100(4), pp.1503-1510.
Danraka, A., Ikebudu, I., Daniel-Ebune, E., Tikare, O., & Abdulmujeeb, A. (2022). A cross- sectional survey on blood pressure screening at
World Hypertension Day Commemoration Health Outreach among adult residents of Life Camp, Abuja, Nigeria: https://doi.org/10.51412/psnnjp.2022.40. The Nigerian Journal of Pharmacy, 56 (2). https://psnnjp.org/index.php/home/article/view/302
Chuemere, A. N., Olorunfemi, O. J., Nwogu, J. U., Mmom, O. F., Agbai, E. O., and Vurey, V. V. (2015). Correlation between blood group, hypertension, obesity, diabetes, and combination of prehypertension and pre-diabetes in school aged children and adolescents in Port Harcourt. IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences, 14(12), 83-89.
Lopez-Jimenez, F., Almahmeed, W., Bays, H., Cuevas, A., Di Angelantonio, E., le Roux, C.W., Sattar, N., Sun, M.C., Wittert, G., Pinto, F.J. and Wilding, J.P., 2022. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: mechanistic insights and management strategies. A joint position paper by the World Heart Federation and World Obesity Federation. European journal of preventive cardiology, 29(17), pp.2218-2237.
Loef, M. and Walach, H., 2012. The combined effects of healthy lifestyle behaviors on all cause mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Preventive medicine, 55(3), pp.163-170.
Downloads
Views | PDF Downloads:
1412
/ 274
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The Nigerian Journal of Pharmacy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.


