A new bicyclic azepinoindole alkaloid from the seed cotyledon of <i>Chrysophyllum albidum</i> G. Don-Holl. (Sapotaceae)
Keywords:
azepinoindole alkaloids, Chrysophyllum albidum, Sapotaceae, anticancer activity, beta carbolinesAbstract
Background: Previous investigation in our laboratory revealed the presence of beta carbolines in the seed cotyledon of Chrysophyllum albidum (G. Don), Sapotaceae. Recent developments underscore the utility of repurposing antifungal compounds for anticancer activities. As a continuation of our search for antcancer compounds from Nigerian medicinal plants, the seed cotyledons of Chrysophyllum albidum (G. Don), Sapotaceae was re-investigated for the expression of anti-tumour compounds.
Methods: The seed cotyledons of C albidum were air-dried under shade for two weeks after which they were powdered using Hammer mill. The powdered seed cotyledons was extracted with methanol (100 %). The methanol (MeOH) extract was defatted and subjected to solid phase extraction using Strata C-18-E cartridge (Phenomenex, USA) (20 g), to obtain four fractions (CA1-CA4). Further purification of CA1 on silica gel (mesh 200-400) gave pure compounds 1 and 2. Both compounds were subjected to extensive spectroscopic analysis using NMR (1H- and 13C-NMR, 1H–1H COSY, DEPT, HMQC, HMBC) and ESI-MS spectra. Cell viability assay was carried out on the identified compounds using MTT assay.
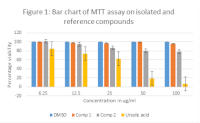
Results: Compounds 1 and 2 were named (provisionally) as albidumine, a new azepinoindole alkaloid, and bamindolinol, a new fused beta carboline, respectively. The compounds did not show any significant effect against human cervical adenocarcinoma (HeLa) cell line in the cytotoxicity assay.
Conclusion: Two new beta carbolines were identified from the seed cotyledon of C albidum for the first time.
References
Lindsay AC, Kim SH, and Sperry J (2018) Non- monoterpenoid azepinoindole alkaloids. Natural Product Reports 33: 1347-1382.
Maryanoff BE, McComsey DF, Martin GE, Shank RP (1998) Azepinoindole derivatives with high affinity for brain dopamine and serotonin receptors. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 21;8(8):983-8.
Robbers JE, Floss HG (1969) Clavicipitic acid, a new 4-substituted indolic amino acid obtained from submerged cultures of the ergot fungus. Tetrahedron Letter(23): 1857 - 1858. doi:10.1016/s0040-4039(01)88031-x.
Blackman AJ, Hambley TW, Picker K, Taylor WC and Thirasasana N (1987) A novel alkaloid from the marine bryozoan hincksinoflustra denticulate. Tetrahedron Letter 28: 5561–5562
King GS, Waight ES, Mantle PG and Szczyrbak CA (1977) The structure of clavicipitic acid, an azepinoindole derivative from Claviceps
fusiformis. Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 1 2099-2103
Qu SJ, Liu QW, Tan CH, Jiang SH, Zhu DY (2006) New indole N-oxide alkaloids from Evodia fargesii. Planta Medica 72(3):264-266.
doi:10.1055/s-2005-873195.
Imaganoa Uruaee (2013) “Chemical and Antioxidant Evaluation of Star Apple Fruit (Chrysophyllum albidum) Crude Extracts”.
Planta Medica: 79-83.
Anang MA, Oteng-Peprah M, Opoku-Boadu K (2019) Extraction and Characterisation of African Star Apple (Chrysophyllum albidum) Seed Oil and the Adsorptive Properties of the Fruit Shell in Ghana. International Journal of Food Science 2019:4959586. Published 2019 Apr 1. doi:10.1155/2019/4959586
Idowu TO, Onawunmi GO, Ogundaini AO, Adesanya SA (2003). Antimicrobial constituents of Chrysophyllum albidum seed cotyledons. Nigerian Journal of Natural Products and Medicines 7:33- 36
Weng N, Zhang Z, Tan Y, Zhang X, Wei X, Zhu Q (2023). Repurposing antifungal drugs for cancer therapy. Journal of Advanced Research 48:259-273. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2022.08.0184.
Taiwo BJ, Popoola TD, van Heerden FR, Fatokun AA (2020) Pentagalloylglucose, isolated from the leaf extract of Anacardium occidentale L., could elicit rapid and selective cytotoxicity in cancer cells. BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies 20(1):287. Published 2020 Sep 21. doi:10.1186/s12906-020-03075-3
Huang L. and Yu DQ (1998) Application of Ultraviolet Spectrum in Organic Chemistry, Part II, pp. 132–137, Science Press, Beijing.
Wang JY, Li XG, Yang XW (2006) Ginsenine, a new alkaloid from the berry of Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer. Journal of Asian Natural Products
Research 8(7): 605 - 608. doi:10.1080/10286020500208444
Wang T, Zhao J, Li X, et al (2016) New Alkaloids from Green Vegetable Soybeans and Their Inhibitory Activities on the Proliferation of Concanavalin A-Activated Lymphocytes. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 64(8):1649-1656. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.5b06107
Downloads
Views | PDF Downloads:
523
/ 182
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The Nigerian Journal of Pharmacy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.


