Evaluation of Acute Dermal Toxicity and Acute Oral Toxicity of Neurovoral<sup>®</sup>Cream and Tea Extract in Rats
Keywords:
dermal toxicity, erythema, hyperemia, tea extract, Traditional African MedicineAbstract
Herbal products have become a common remedy used in treatment and management of many diseases. The safety ascribed to natural products because of their origin is now doubtful as side effects and toxicities have been recorded. The aim of the study is to determine acute dermal toxicity and acute oral toxicity of Neurovoral® cream and tea extract.
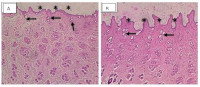
Thirty albino rats were used to investigate the acute dermal toxicity (12) and acute oral toxicity (18) of Neurovoral® cream and tea respectively. Neurovoral® cream (0.5 g) was applied to the trimmed dorsal area of the trunk of rats, signs of toxicity (erythema, oedema, irritation) were observed periodically at 24, 28 and 72 h, and again after 14 days. The extract from the tea was administered at 2000 and 5000 mg/kg, and the rats were observed for the first 6 hours, and there after daily for 14 days. th All the animals were euthanised at the 14 day and vital organs (skin, kidney, liver, brain) were collected for subsequent histological analysis. Dermal toxicological report showed negligible erythema during the period of application of cream, and acute oral administration of 5000 mg/kg did not result in death or any significant toxicity signs. There was no significant alteration in the histology of organs observed. The study results indicated that Neurovoral® cream and tea are relatively safe and non-toxic to rats in acute exposure.
References
1. Kurn, SJ, Shook S. Herb and Nutrients for Neurologic Disorder: Treatment strategies for Alzheimer`s Parkinson, Stroke, Multiple Sclerosis, Migraine and Seizures. Simon and Schuster; 2016 June 16
2. Wannissorn B, Jarikasem S, Siriwangchai T, Thubthimthed S. Antibacterial properties of essential oils from Thai medicinal plants. Fitot e r api a . 2005 Ma r 1;76(2):233-6. doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2004.12.009
3. Yayesh Limenih YL, Shemsu Umer SU, Messay Wolde-Mariam MW. Ethnobotanical study on traditional medicinal plants in Dega Damot Woreda, Amhara Region, North Ethiopia.
4. Ding X, Han C, Hu W, Fu C, Zhou Y, Wang Z, Xu Q, Lv R, He C, Zuo Z, Huang J. Acute and subacute safety evaluation of black tea extract (herbt tea essences) in mice. Toxics. 2022 May 27;10(6):286.
5. Xu J, Yan B, Zhang L, Zhou L, Zhang J, Yu W, Dong X, Yao L, Shan L. Theabrownin induces apoptosis and tumor inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma Huh7 cells through ASK1-JNK-c-Jun pathway. OncoTargets and therapy. 2020 Sep 9:8977-87.
6. Tang GY, Meng X, Gan RY, Zhao CN, Liu Q, Feng YB, Li S, Wei XL, Atanasov AG, Corke H, Li HB. Health functions and related molecular mechanisms of tea components: an update review. International journal of molecular sciences. 2019 Dec 8;20(24):6196.
7. Bello I, Bakkouri AS, Tabana YM, Al-Hindi B, AlMansoub MA, Mahmud R, Asmawi MZ. Acute and sub-acute toxicity evaluation of the methanolic extract of Alstonia scholaris stem bark. Medical sciences. 2016 Mar 8;4(1):4.
8. Wang D, Xiao R, Hu X, Xu K, Hou Y, Zhong Y, Meng J, Fan B, Liu L. Comparative safety evaluation of Chinese Pu-erh green tea extract and Pu-erh black tea extract in Wistar rats. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2010 Jan 27;58(2):1350-8.
9. Gardner EJ, Ruxton CH, Leeds AR. Black tea–helpful or harmful? A review of the evidence. European journal of clinical nutrition. 2007 Jan;61(1):3-18.
10. Lulekal E, Tesfaye S, Gebrechristos S, Dires K, Zenebe T, Zegeye N, Feleke G, Kassahun A, Shiferaw Y, Mekonnen A. Phytochemical analysis and evaluation of skin irritation, acute and subacute toxicity of Cymbopogon citratus essential oil in mice and rabbits. Toxicology reports. 2019 Jan 1;6:1289-94.
11. Guideline O. Acute Oral Toxicity‐Acute Toxic Class Method. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals.
12. Awodele O, Awolola A, Oladimeji-Salami JA, Ayinde OO. Investigation of Acute Dermal Toxicity of Some Hydroquinone Containing Cosmetics in Rats. University of Lagos Journal of Basic Medical Sciences. 2022 Sep 2;4(8).
13. Rispin A, Farrar D, Margosches E, Gupta K, Stitzel K, Carr G, Greene M, Meyer W, McCall D. Alternative methods for the median lethal dose (LD50) test: the up-and-down procedure for acute oral toxicity. ILAR journal. 2002 Jan 1;43(4):233-243.
14. Alavi A, Sibbald RG, Ladizinski B, Saraiya A, Lee KC, Skotnicki-Grant S, Maibach H. Woundrelated allergic/irritant contact dermatitis. Advances in skin & wound care. 2016 Jun 1;29(6):278-86.
15. Mathur AK. Safety of industrial chemicals and finished product. Anil Aggrawal's Internet Journal of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology. 2005;6(1).
16. Han SM, Lee GG, Park KK. Acute dermal toxicity study of bee venom (Apis mellifera L.) in rats. Toxicological research. 2012 Jun;28(2):99-102.
17. Guaouguaou FE, Taghzouti K, Oukabli M, Masrar A, Chabraoui L, Bouabdellah M, Es-Safi NE. Acute and subchronic oral and dermal toxicological studies of salvia verbenaca extracts in mice and rats. Journal of Herbs, Spices & Medicinal Plants. 2019 Jan 2;25(1):33-42.
18. Gatne M, Tambe K, Adarsh A, Ravikanth K. Acute dermal irritation study of polyherbal gel mastilep in rabbits.
19. Hothorn LA, Hajian G. Biostatistics in toxicology. Toxicology. 1999 Jan 1:25-41.
20. Ramaiah SK. Preclinical safety assessment: current gaps, challenges, and approaches in identifying translatable biomarkers of druginduced liver injury. Clinics in Laboratory Medicine. 2011 Mar 1;31(1):161-72.
Downloads
Views | PDF Downloads:
576
/ 136
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.


