Stable High-Loading of All-trans Retinoic Acid in Nanoliposomes Achieved Through Optimized pH and Antioxidant Incorporation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51412/psnnjp.2025.23Keywords:
Vaccine, adjuvants, All-trans retinoic acid, GLA, 3M052, stabilityAbstract
Background: All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) has been shown to have an immunomodulatory activity that could be explored to develop adjuvants for vaccination against intestinal or mucosal infections. However, progress has been limited by the poor chemical stability of ATRA and the high concentrations required. This study aimed to incorporate high-dose ATRA in a previously developed nanoliposome containing Toll-like receptor agonists (TLR) - (GLA) and 3M-052, optimising the excipient composition and the physicochemical stability of ATRA.
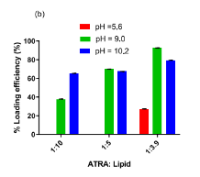
Method: Different ratios of ATRA: lipid, as well as different pH values, were explored to enable the incorporation of up to 3 mg/mL ATRA in the liposomal formulation. A hydrophobic antioxidant, α- tocopherol, was evaluated for its capacity to increase the chemical stability of ATRA within the liposomes. The particle size was determined by dynamic light scattering, and ATRA content was determined by HPLC with a diode array detector. Stability was monitored under normal and stressed conditions.
Results: Maximum ATRA incorporation and nanoliposome stability occurred at low ATRA: lipid ratio, elevated pH, and with the inclusion of α-tocopherol. This study showed that the formulation of ATRA depends on the ATRA: lipid ratio, the pH of the hydrating solvent, and the incorporation of α- tocopherol, which enhances the loading efficiency of ATRA and protects the formulation against oxidation and photodegradation.
Conclusion: Nevertheless, whereas the optimised liposome formulation remained suitable for TLR7/8 agonist (3M-052) stability, a significant loss in the TLR4 agonist (GLA) content occurred following manufacture, likely due to the high pH condition.
References
Mora JR, Iwata M, Von Andrian UH (2008) Vitamin effects on the immune system: Vitamins A and D take centre stage. Nature Reviews
Immunology, 8(9):685-98. doi:10.1038/nri2378
Manicassamy S, Pulendran B (2009) Retinoic acid-dependent regulation of immune responses by dendritic cells and macrophages. Seminars in Immunology.
Mucida D, Park Y, Kim G, Turovskaya O, Scott I, Kronenberg M, Cheroutre H (2007) Reciprocal TH17 and regulatory T cell differentiation mediated by retinoic acid. Science, 317(5835):256-60. doi:10.1126/science.1145697
Iwata M, Hirakiyama A, Eshima Y, Kagechika H, Kato C, Song SY (2004) Retinoic acid imprints gut-homing specificity on T cells. Immunity,
(4):527-38. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2004.08.011
Hall JA, Grainger JR, Spencer SP, Belkaid Y (2011) The role of retinoic acid in tolerance and immunity. Immunity, 35 (1): 13 - 22.
doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2011.07.002
Hall JA, Cannons JL, Grainger JR, Dos Santos LM, Hand TW, Naik S, Wohlfert EA, Chou DB, Oldenhove G, Robinson M, et al (2011) Essential
role for retinoic acid in the promotion of CD4+ T cell effector responses via retinoic acid receptor alpha. Immunity, 34 (3): 435 - 47.
doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2011.03.003
Klebanoff CA, Spencer SP, Torabi-Parizi P, Grainger JR, Roychoudhuri R, Ji Y, Sukumar M, Muranski P, Scott CD, Hall JA, et al (2013) Retinoic acid controls the homeostasis of pre-cDC-derived splenic and intestinal dendritic cells. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 210 (10): 1961-76. doi:10.1084/jem.20122508
Tan X, Sande JL, Pufnock JS, Blattman JN, Greenberg PD (2011) Retinoic Acid as a Vaccine Adjuvant Enhances CD8+ T Cell Response and
Mucosal Protection from Viral Challenge. Journal of Virology, 85 (16): 8316 - 27. doi:10.1128/jvi.00781-11
Abhyankar MM, Noor Z, Tomai MA, Elvecrog J, Fox CB, Petri WA (2017) Nanoformulation of synergistic TLR ligands to enhance vaccination against Entamoeba histolytica. Vaccine, 35 (6): 916 - 922. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.12.057
Lisulo MM, Kapulu MC, Banda R, Sinkala E, Kayamba V, Sianongo S, Kelly P (2014) Adjuvant potential of low dose all-trans retinoic acid during oral typhoid vaccination in Zambian men. Clinical and Experimental Immunology, 175(3):468-75. doi:10.1111/cei.12238
Christensen D, Bøllehuus Hansen L, Leboux R, Jiskoot W, Christensen JP, Andersen P, Dietrich J (2019) A Liposome-Based Adjuvant Containing Two Delivery Systems with the Ability to Induce Mucosal Immunoglobulin A Following a Parenteral Immunization. ACS Nano, 13(2): 1116 - 1126. doi:10.1021/acsnano.8b05209
Ozpolat B, Lopez-Berestein G, Adamson P, Fu CHJ, Williams AH (2003) Pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered liposomal all-trans-retinoic acid (atra) and orally administered atra in healthy volunteers. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 6(2):292-301.
Szuts EZ, Harosi FI (1991) Solubility of retinoids in water. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 287(2):297-304. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(91)90482-X
Selek H, Ünlü N, Orhan M, Irkeç M (2000) Evaluation of retinoic acid ophthalmic emulsion in dry eye. European Journal of Ophthalmology, 10 (2): 121 - 127. doi:10.1177/112067210001000205
Giuli MV, Hanieh PN, Giuliani E, Rinaldi F, Marianecci C, Screpanti I, Checquolo S, Carafa M (2020) Current trends in ATRA delivery for cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics. 12 (8): 707. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics12080707
Olusanya TOB, Ahmad RRH, Ibegbu DM, Smith JR, Elkordy AA (2018) Liposomal drug delivery systems and anticancer drugs. Molecules,
(4): 907. doi:10.3390/molecules23040907
Minò A, Lopez F, Barbaro R, Barile M, Ambrosone L, Colella M (2024) Effects of Anionic Lipo some Delivery of All–Trans–Retinoic Acid on Neuroblastoma Cell Differentiation. Biomimetics, 9 (5): 257. doi:10.3390/biomimetics9050257
Lim SJ, Lee MK, Kim CK (2004) Altered chemical and biological activities of all-trans retinoic acid incorporated in solid lipid nanoparticle powders. Journal of Controlled Release, 100 (1): 53 - 61. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2004.07.032
Sercombe L, Veerati T, Moheimani F, Wu SY, Sood AK, Hua S (2015) Advances and challenges of liposome assisted drug delivery. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 6: 286. doi:10.3389/fphar.2015.00286
Hsi SL, Surman P, Al-Kassas R (2019) Development of a stability-indicating UPLC method for determination of isotretinoin in bulk drug. Pharmaceutical Development and Technology, 17; 9 (8): e18405. doi:10.1080/10837450.2018.1454469
Abhyankar MM, Orr MT, Kinsey R, Sivananthan S, Nafziger AJ, Oakland DN, Young MK, Farr L, Uddin MJ, Leslie JL, et al (2021) Optimizing a Multi-Component Intranasal Entamoeba Histolytica Vaccine Formulation Using a Design o f Experiments Strategy. Frontiers in Immunology, 12: 683157. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.683157
Noy N (1992) The ionization behavior of retinoicacid in aqueous environments and bound to serum albumin. BBA – Biomembranes, 1106(1):151-8. doi:10.1016/0005-2736(92)90233-C
Noy N (1992) The ionization behavior of retinoic acid in lipid bilayers and in membranes. BBA – Biomembranes, 1106 (1): 159 - 164. doi:10.1016/0005-2736(92)90234-D
Errico C, Gazzarri M, Chiellini F (2009) A novel method for the preparation of retinoic acid-loaded nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 10 (5): 2336 - 2347. doi:10.3390/ijms10052336
Rodsamai T, Chaijan M, Rodjan P, Tamman A, Supaweera N, Yin M, Kim SR, Panpipat W (2025) Design and Bioanalysis of Nanoliposome Loaded with Premium Red Palm Oil for Improved Nutritional Delivery and Stability. Foods, 14(4):566. doi:10.3390/foods14040566
Ko S, Lee S-C (2010) Effect of nanoliposomes on the stabilization of incorporated retinol. African Journal of Biotechnology 9(37):6158–6161. http://www.academicjournals.org/AJB
Kulkarni SB, Betageri GV, Singh M (1995) Factors affecting microencapsulation of drugs in liposomes. Journal of Microencapsulation, 12 (3) :229-46. doi: 10.3109/02652049509010292
Stamp D, Juliano RL (1979) Factors affecting the encapsulation of drugs within liposomes. Canadian Journal of Physiology and
Pharmacology. 57(5). doi:10.1139/y79-081
Lasic DD (1997) Liposomes in Gene Delivery. London: CRC Press.
Van Den Brink-Van Der Laan E, Antoinette Killian J, De Kruijff B (2004) Nonbilayer lipids affect peripheral and integral membrane proteins via changes in the lateral pressure profile. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Biomembranes, 1666 (1 - 2): 275 - 288.
doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.06.010
Sewald N, Jakubke HD (2009) Peptides: Chemistry and Biology: Second Edition. doi:10.1002/9783527626038
Kayser O, Warzecha H (2012) Pharmaceutical Biotechnology: Drug Discovery and Clinical Applications. doi:10.1002/9783527632909
Antimisiaris SG, Mourtas S, Gregoriadis G (2007) Liposome Technology, Volume III: From Diagnosis to Therapy, Methods in Molecular
Biology series. Humana Press.
Grace VMB, Wilson DD, Guruvayoorappan C, Danisha JP, Bonati L (2021) Liposome nano- formulation with cationic polar lipid DOTAP and cholesterol as a suitable pH-responsive carrier for molecular therapeutic drug (all-trans retinoic acid) delivery to lung cancer cells. IET Nanobiotechnology. 15 (4): 380 – 390. doi:10.1049/nbt2.12028
Peetla C, Stine A, Labhasetwar V (2009) Biophysical interactions with model lipid membranes: Applications in drug discovery and drug delivery. In: Molecular Pharmaceutics. Vol. 6 . [place unknown]; p. 1264 – 1276. doi:10.1021/mp9000662
Lee Y, Thompson DH (2017) Stimuli-responsive liposomes for drug delivery. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology, 9(5):10.1002/wnan.1450. doi:10.1002/wnan.1450
Gaohua L, Miao X, Dou L (2021) Crosstalk of physiological pH and chemical pKa under the umbrella of physiologically based
pharmacokinetic modeling of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity. Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism &
Toxicology. 17 (9): 1103 – 1124. doi:10.1080/17425255.2021.1951223
Carlotti ME, Rossatto V, Gallarate M (2002) Vitamin A and vitamin A palmitate stability over time and under UVA and UVB radiation. International Journal of Pharmaceutic, 40(1-2):85-94. doi:10.1016/S0378-5173(02)00128-X
Manconi M, Valenti D, Sinico C, Lai F, Loy G, Fadda AM (2003) Niosomes as carriers for tretinoin: II. Influence of vesicular incorporation on tretinoin photostability. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 260 (2): 261 - 72. doi:10.1016/S0378-5173(03)00268-0
Brisaert MG, Everaerts I, Plaizier-Vercammen JA (1995) Chemical stability of tretinoin in dermatological preparations. Pharmaceutica Acta Helvetiae. 70 (2):161-166. doi:10.1016/0031-6865(95)00016-3
Brisaert M, Gabriëls M, Matthijs V, Plaizier-Vercammen J (2001) Liposomes with tretinoin: A physical and chemical evaluation. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 26(5-6):909-17. doi:10.1016/S0731-7085(01)00502-7
Lombardo D, Kiselev MA (2022) Methods of Liposomes Preparation: Formation and Control Factors of Versatile Nanocarriers for Biomedical and Nanomedicine Application. Pharmaceutics, 14 (3): 543. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14030543
Lee CM, Jeong HJ, Park JW, Kim J, Lee KY (2008) Temperature-induced release of all-trans-retinoic acid loaded in solid lipid nanoparticles for topical delivery. Macromolecular Research, 16 (8): 682-685. doi:10.1007/BF03218581
Downloads
Views | PDF Downloads:
406
/ 136
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The Nigerian Journal of Pharmacy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.


