Anxiolytic and antiamnesic potentials of <i>Terminalia</i> A. Chev (Combretaceae) stem and root bark methanol extracts in mice.
Keywords:
Terminalia ivoriensis, root bark, stem bark, anxiolytic, antiamnesic effectsAbstract
Background: Terminalia ivorensis (Chev) stem bark is used in combating mental illnesses in African traditional medicine. Previous studies demonstrated its antipsychotic properties but there are no documented reports on the anxiolytic and antiamnesic properties of Terminalia ivorensis. Hence, this study investigated the anxiolytic and antiamnesic potentials of methanol stem bark and root bark
extracts of T. ivorensis in mice.
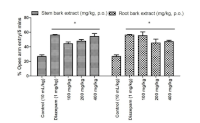
Methods: The anxiolytic potentials of stem and root bark methanol extracts at 100, 200 and 400 mg/kg b.w were investigated using mouse model of anxiety (elevated plus maze test), while the antiamnesic potentials were assessed using mouse model of short term memory assessment (Y-maze test).
Results: The stem and root bark methanol extracts at all the tested doses, significantly (p≤0.05) elongated the percentage number of entries into the open arm of the elevated plus maze, while the duration of stay on the open arm of the elevated plus maze was only significant (p≤0.05) at 100 mg/kg for stem bark extract. Stem and root bark extracts, at all the tested doses, significantly (p≤0.05) reduced the anxiety indices of mice indicative of antianxiety potentials. Both extracts showed significant (p≤0.05) dose-dependent decrease in percentage correct alternations compared to the scopolamine control group indicating antiamnesic effect.
Conclusion: This study revealed that stem and root bark extracts may possess anxiolytic and antiamnesic effects in mice which justify its use in treating mental illnesses in traditional medicine.
References
Saki K, Bahmani M, Rafieian-Kopaei M (2014) The effect of most important and medicinal plants on two important psychiatric disorders (anxiety and depression)—a review. Asian Pacific Journal o f Tropical Medicine 7(1): 34 - 42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60201-7
Bandelow B, Michaelis S (2015) Epidemiology of anxiety disorders in the 21st century. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience 7(3):327–335. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2015.17.3/bbandelow
Kessler RC, Berglund P, Dernier O, Jin R, Merikangas KR, Walters EE (2005) Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of
DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Archive of General Psychiatry 62(6):593–602. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.62.6.593
Grant BF, Hasin DS, Stinson FS, Dawson DA, June Ruan W, Goldstein RB, Smith S M , S a h a TD, Huang B (2005) Prevalence, correlates, co-morbidity, and comparative disability of DSM-IV generalized anxiety disorder in the USA: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on alcohol and related conditions. Psychological Medicine 35: 1747–1759. doi:10.1017/S0033291705006069
Amali MO, Atunwa SA, Omotesho QA, Oyedotun EO, Olapade AI (2020) Assessment of anxiolytic potential and acute toxicity study of Combretum micranthum G. Don. leaves (Combretaceae). Journal of Medicinal Plants for Economic Development 4(1):97. doi: https://doi.org/10.4102/jomped.v4i1.97.
Ströhle A, Gensichen J, Domschke K (2018) The Diagnosis and Treatment of Anxiety Disorders. Deutsches Arzteblatt International 155(37):611- 620. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2018.0611.
Onete OU (2020) Anxiety disorder and mental health of adolescents in contemporary Nigeria. Journal of Science Engineering and Technology 7(1):110-115
Stein MB, Stein DJ (2008) Social anxiety disorder. Lancet 371 (9618): 1115 - 1125. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60488-02
Moser DK (2007). The rust of life: Impact of anxiety on cardiac patients. American Journal of Critical Care 16(4): 361–369.
Koen N, Stein DJ (2011). Pharmacotherapy of anxiety disorders: A critical review. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience 13(4): 423-437. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2011.13.4/nkoen
Nutt DJ, Ballenger JC, Sheehan D, Wittchen HU (2022) Generalized anxiety disorder: comorbidity, comparative biology and treatment. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 5(4): 315-325. doi: 10.1017/S1461145702003048
Tyrer P, Baldwin D (2006). Generalised anxiety disorder. Lancet 368 (9553): 2156-2166. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69865-6
Khan A, Akram M, Thiruvengadam M, Daniyal M, Zakki SA, Munir N, Zainab R, Heydari M, Mosavat SH, Rebezov M, Shariati MA (2022) Anti-anxiety properties of selected medicinal plants. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology 23(8):1041-1060. doi: 10.2174/1389201022666210122125131
Sanabria E, Cuenca RE, Esteso MÁ, Maldonado M (2012) Benzodiazepines: Their use either as essential medicines or as toxics Substances.Toxics 9(2):25. doi: 10.3390/toxics9020025
Edinoff AN, Nix CA, Odisho AS, Babin CP, Derouen AG, Lutfallah SC, Cornett EM, Murnane KS, Kaye AM, Kaye AD (2022) Novel designer benzodiazepines: comprehensive review of evolving clinical and adverse effects. Neurology International 14(3):648-663.
3390/neurolint14030053
Edinoff AN, Nix CA, Hollier J, Sagrera CE, Delacroix BM, Abubakar T, Cornett EM, Kaye AM, Kaye AD (2021). Benzodiazepines: Uses, Dangers, and Clinical Considerations. Neurology International 13(4):594-607. doi: 10.3390/neurolint13040059.
Singh MF, Singh VV, Shalini R, Himani B, Anupam B (2013) Memory enhancing effect of mirtazapine with ascorbic acid on scopolamine
induced amnesia in rats. Guru Drone Journal of Pharmaceutical Research International 1(1): 29- 38.https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:152048041
Briggs R, Kennelly SP, O'Neill D (2016). Drug treatments in Alzheimer's disease. Clinical Medicine (Lond) 16(3): 247- 253. http://doi.org/:10.7861/clinmedicine.16-3-247.
Panegyres PK. (2004) The contribution of the study of neurodegenerative disorders to the understanding of human memory. QJM: International Journal of Medicine 97(9):555–567. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hch096
Tanwar A, Bafna PA, Bafna AR (2014) Anti- amnesic effect of aqueous extract of Crataeva nurvala stem bark in scopolamine induced
amnesia. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science 4(9):66-72.doi: 10.7324/JAPS.2014.40912
Ogunwande IA, Ascrizzi R and Guido F (2019) Essential oil composition of Terminalia ivorensis A. Chev. flowers from Northern Nigeria. Trends in Phytochemical Research 3(1): 77-82.
Burkill HM (1985) Entry for Lasiurus hirsutus (Forssk.) Boiss. [family POACEAE]. In: The useful plants of West tropical Africa, 2nd edition.
Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, 1:960-97. https://plants.jstor.org/collection/UPWTA
Akinyemi KO, Oluwa OK, Omomigbehin EO(2006) Antimicrobial activity of crude extracts of three medicinal plants used in south-west
Nigerian folk medicine on some food borne bacterial pathogens. African Journal of Traditional Complementary and Alternative Medicine 3(4):13-22. doi: 10.4314/ajtcam.v3i4.31173
Sitapha O, Elisee KK, Joseph DA (2013) Antifungal activities of Terminalia ivorensis A. Chev. bark extracts against Candida albicans and Aspergillus fumigatus. Journal of Intercultural Ethnopharmacology 2(1):49-52. doi: 10.5455/jice.20121205083931
Lawal IO, Uzokwe NE, Igboanugo AB, Adio AF, Awosan EA, Nwogwugwu JO (2010) Ethno- medicinal information on collation and identification of some medicinal plants in Research Institutes of South-west Nigeria. African Page| 410 Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 4:001-007. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:73072898
Moomin A, Mensah KB, Forkuo AD, Adu-Gyamfi PKT, Ansah C (2020). Ethanolic stem bark extract of Terminalia ivorensis A. Chev. protects against potassium dichromate–induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Scientific African 08:e00410. doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00410
Ponou BK, Teponno RB, Ricciutelli M, Nguelefack TB, Quassinti L, Bramucci M, Lupidi G, Barboni L, Tapondjou LA (2011) Novel 3-oxo-and 3,24- dinor-2,4-secooleanane-type triterpenes from Terminalia ivorensis A. Chev. C h e m i s t r y and Biodiversity 8(7):1301-1309. doi:10.1002/cbdv.201000145.
Adeoluwa OA, Aderibigbe AO, Agu GO, A d e w o l e F A , E d u v i e r e AT ( 2 0 1 5 ) Neurobehavioural and analgesic properties of
ethanol bark extract of Terminalia ivorensis A Chev. (Combrataceae) in mice. Drug Research (Stuttg). 65(10):545-551. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1394417.
Av o s e h N O , A d e b a y o M A , L a w a l O A , Ogunwande IA (2018). Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of Terminalia ivorensis. South Asian Research Journal of Natural Product 1(3):1-8. doi:10.9734/SARJNP/2018/43614
Ben-Azu B, Aderibigbe AO, Adeoluwa OA, Iwalewa EO (2016) Ethanol extracts of Terminalia ivorensis (Chev A.) stem bark attenuates the
positive, negative and cognitive symptoms of psychosis in experimental animal models. British Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 12(6):1-14. doi: 10.9734/BJPR/2016/28629.
Mani V, Sajid S, Rabbani SI, Alqasir AS, Alharbi HA, Alshumaym A (2021). Anxiolytic-like and antidepressant-like effects of ethanol extract of Terminalia chebula in mice. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine 11(6):493-502. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2021.04.003.
Chandrashekar R, Manohar V.R, Poovizhi BR (2017) Attenuation of anxiety on acute administration of aqueous extract of Terminalia
belerica fruit pulp in swiss albino mice. International Journal of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology 6 ( 2 ) : 3 0 3 – 3 0 7 . https://doi.org/10.18203/2319-2003.ijbcp20170319
Kim, MS., Lee, D.Y., Lee, J. Kim HW, Sung SH, Han JS, Jeon WK, WK (2018) Terminalia chebula extract prevents scopolamine-induced amnesia via cholinergic modulation and anti-oxidative effects in mice. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 18:136.doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2212-y.
R e d d y N V L S V, R a j u G M , G o u d R M , Shabnamkumari T (2020) Neuroprotective activity of methanolic extract of Terminala
bellerica fruit against aluminium chloride and haloperidol induced amnesia in mice. Journal of Young Pharmacist 12(2):87-90. doi:10.5530/jyp.2020.12s.53
NIH. (1985). Guide for the use of laboratory animals. DHHS, PHS, NIH Publication No. 1985:85-23 (Revised).
Adebayo MA, Akinpelu LA, Okwuofu EO, Ibia D E , L a w s o n - J a c k A F, I g b e I ( 2 0 2 0 ) Anticonvulsant, antiamnesic and anxiolytic
activities of methanol leaf extract of Bambusa vulgaris (Poaceae) in mice. Journal of African Association of Physiological Science 8(2): 149-157. https://www.ajol.info/index.php/jaaps/article/vie w/205716
Bourin M (2015) Animal models for screening anxiolytic-like drugs: a perspective. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience 17(3): 295 - 303. 10.31887/DCNS.2015.17.3/mbourin Murade V, Waghmare A, Pakhare D, Dichayal S, Patil R, Wanjari M, Hase D (2021). A plausible involvement of GABAA/benzodiazepine receptor in the anxiolytic-like effect of ethyl acetate fraction and quercetin isolated from Ricinus communis Linn. leaves in mice. Phytomedicine plus 1(3): 100041. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.phyplu.2021.100041
Akinpelu LA, Adebayo MA, Fajana A, Adeniyi-Akee MA, Ubogu SE, Aminu NS (2019) Phytochemical analyses, anxiolytic and anti-amnesic effect of methanol stem bark extract o f Vitex doniana (Sweet) in mice. Nigerian Journal of Natural Product and Medicine 23: 104-111. doi:10.4314/njnpm.v23i1.14
Downloads
Views | PDF Downloads:
392
/ 145
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The Nigerian Journal of Pharmacy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.


