Effect of physical factors on the antimicrobial efficacy of amoxicillin trihydrate capsules and reconstituted suspension
Keywords:
Amoxicillin, antimicrobial, heat, absorbance, drug content, reconstituted suspensionAbstract
Background: Stability of drugs depends on both environmental factors and drug-related factors. Exposure of medicines to high temperatures during storage or transit could reduce their efficacy thus, shelf life and expiry dates may no longer be guaranteed. The objective of this study was to determine the effect of heat and environmental conditions on the antimicrobial efficacy of amoxicillin trihydrate.
Methods: Five brands of amoxicillin trihydrate capsules and six brands of amoxicillin trihydrate powder for suspension were purchased from retail pharmacies in Abuja, Nigeria. For the capsules, 100 μg/mL of the different brands and 25, 50 and 100 μg/mL of reference standard were prepared and subjected to heat treatment at different temperatures (25, 40, 60 and 80 oC) for 30 min. Each of the amoxicillin trihydrate powder for suspension was reconstituted in water and subjected to different storage conditions for 7 days. The UV absorbance of the reference amoxicillin trihydrate was determined while the potencies of heat-treated amoxicillin capsules and stored suspensions were evaluated by agar diffusion method.
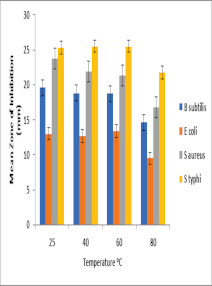
Results: At 25 and 40 oC there was no signifificant change in the antimicrobial efficacy of amoxicillin, however as the temperature increased to 80 oC there was a reduction in the zones of inhibition against the test organisms. The absorbance readings of the heat-treated reference amoxicillin trihydrate powder gradually increased with increase in temperature. There was no significant (p< 0.05) reduction in the antimicrobial effffects of the reconstituted suspensions within 7 days of testing.
Conclusion:The antimicrobial stability of amoxicillin can be affected by exposure to extreme heat
References
Briscoe CJ, Hage DS. Factors affecting the stability of drugs and drug metabolites in biological matrices. Bioanalysis. 2009 Apr;1(1):205-20. doi: 10.4155/bio.09.20. PMID: 21083197.
Medecins San Frontieres (MSF) (2019): Essential drugs- Practical guideline: Part two- Drug quality and storage, pp 499-501. ISBN 978-2-37585-051-0.
Abaje IB and Oladipo EO. (2019). Recent changes in the temperature and rainfall Conditions Over
Kaduna State, Nigeria. Ghana Journal of Geography Vol. 11(2), 2019 pages 127- 157.
Orisakwe I, Nwofor O, Njoku C and Ezedigboh U. (2017). On the Analysis of the Changes in the Temperatures over Abuja, Nigeria. Journal of Physical Science and Environmental Studies. 3. 8 - 17.
Eludoyin O, Adelekan IO, Webster R and Eludoyin AO. (2013): Air temperature, relative humidity, climate regionalization and thermal comfort of Nigeria. International Journal of Climatology.; 34: 2000 - 2018. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3817
Franje, CA, Chang, S, Shyua, C., Davis, J. L., Leea, Y., Leed, R., Change, C., Choua, C. (2010): Differential heat stability of amphenicols characterized by structural degradation, mass spectrometry and antimicrobial activity. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 53: 869 – 877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2010.06.013
Holt JG, Kreig NR, Sneath PHA, Stanley JT and Williams ST. (1994). Bergeys Manual of Determinative Microbiology, Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, 9th edition, Md, USA, 558 - 571.
Svahn O and Björklund E (2015): Thermal stability assessment of antibiotics in moderate temperature and subcritical water using a pressurized dynamic flow-through system. International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies 11 (4): 872-880.
Aboh MI, Amaeze N, Ikeji I and Oladosu PO. (2021). Effect of abiotic factors on the antifungal
activity of Lactobacillus strains isolated from commercial dairy and fermented foods from Federal
Capital Territory, Nigeria. European Journal of Nutrition & Food Safety, 13 (1): 70 - 78. https://doi.org/10.9734/ejnfs/2021/v13i130350
Prakash K, Narayana R, Shanta K and Lakshmi N. (2008). Spectrophotometric estimation of amoxicillin trihydrate in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage form. E J Chem, 5:1114-1116.
Justesen US, Acar Z, Olsson K, Jensen TG, Kerrn MB, Skov RL, Gahrn-Hansen B (2013). Comparison
of Rosco Neo-Sensitabs with Oxoid paper disks in EUCAST disk diffusion antimicrobial susceptibility
testing on Mueller–Hinton agar. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 32
(5): 621-625. hƩps://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-012-1785-5
Stanley CN and Igala SE. (2017). Effect of different storage conditions on the stability and efficacy of some reconstituted oral antibiotic suspensions sold in Port Harcourt, Nigeria.Journal of Pharmaceutical Research International 20(3): 1-10 https//doi.org//:10.9734/JPRI/2017/38553
Naidoo, KK., Nompuku, P, Mkalali, SN., Shabangu, K., Nkabinde, L., Singh, V. (2006) 'Post-Marketing Stability Surveillance: Amoxicillin', SA Fam Pract 2006; 48 (66): 14a - d. https://hdl.handle.net/10520/EJC79961
Hsieh MK, Shyu EL, LIuo JW, Franje CW, Huang YJ, Chang SK, Shi PY and Chou CC. (2011). Correlation analysis of heat stability of veterinary antibiotics by structural degradation, changes in antimicrobial activity and genotoxicity. Veterinarni Medicina, 56 (6): 274 – 285. https//doi.org//:10.17221/1548-VETMED
Nwokoye P, Oyetunde O and Akinleye M. (2012). Stability of reconstituted amoxicillin clavulanate
potassium under simulated in-home storage conditions. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical
Science 02 (01): 28-31.
Views | PDF Downloads:
992
/ 384
/ 0
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.


